Structure functions#
This documentation page lists all
All parameterisations derive from the following base class:
-
class Parameterisation : public NamedModule<Parameterisation>#
Subclassed by PartonicParameterisation
Detailed description
Click to show
-
class Parameterisation : public NamedModule<Parameterisation>
Base object for the parameterisation of nucleon structure functions.
Subclassed by PartonicParameterisation
Public Functions
-
inline virtual bool hasW1W2() const
provides modelling for W_1/W_2? Longitudinal/transverse cross section ratio parameterisation used to compute
-
Parameterisation &operator()(double xbj, double q2)
Compute all relevant structure functions for a given
- Parameters:
xbj – [in] Bjorken’s x variable
q2 – [in] Squared 4-momentum transfer (in GeV^2)
-
double F2(double xbj, double q2)
Transverse structure function.
-
double FL(double xbj, double q2)
Longitudinal structure function.
-
double W1(double xbj, double q2)
Longitudinal form factor.
-
double FE(double xbj, double q2)
Electric proton form factor.
-
double FM(double xbj, double q2)
Magnetic proton form factor.
-
double F1(double xbj, double q2)
-
inline const std::string &name() const
Module unique indexing name.
-
inline bool operator==(const SteeredObject &oth) const
Equality operator.
-
inline bool operator!=(const SteeredObject &oth) const
Inequality operator.
-
inline virtual const ParametersList ¶meters() const override
Module user-defined parameters.
-
inline virtual void setParameters(const ParametersList ¶ms) override
Set module parameters.
-
inline void setDescribedParameters(const ParametersList ¶ms_orig)
Set (documented) module parameters.
Public Static Functions
-
static ParametersDescription description()
Generic description for the structure functions.
Friends
-
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream&, const Parameterisation&)
Human-readable dump of the SF parameterisation at this (xBj,Q^2) value.
-
struct Arguments
-
struct Values
Public Members
-
double f2 = {0.}
Last computed transverse structure function value.
-
double fl = {0.}
Last computed longitudinal structure function value.
-
double w1 = {0.}
Longitudinal form factor.
-
double fe = {0.}
Electric proton form factor.
-
double fm = {0.}
Magnetic proton form factor.
-
double f2 = {0.}
-
inline virtual bool hasW1W2() const
Note
All of these may be used and linked against any external code.
The parameterisation types handled in CepGen are listed in the cepgen::StructureFunctionsFactory.
Below, a semi-detailed review of a subset of the modellings handled in CepGen is presented.
Whenever not specified explicitely in the modelling, the
Where this
Hybrid models#
As the name suggests, this class of model combines multiple extrapolation models valid in multiple kinematic ranges into a set of uniform, continuous structure functions.
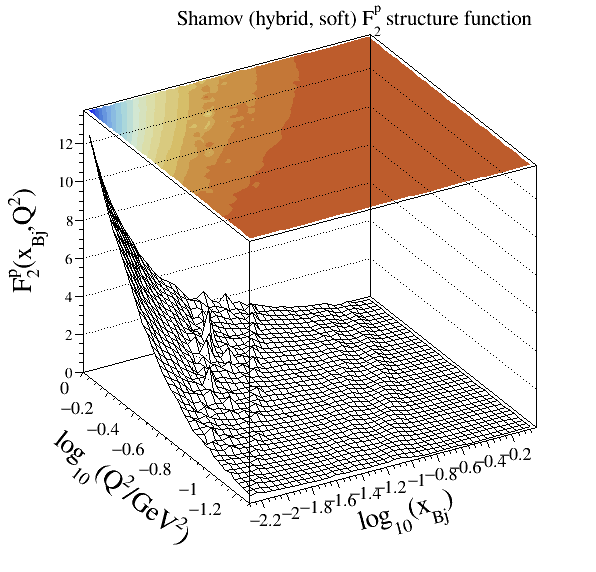
Shamov#
Note
Legacy code:
302Structure functions modelled:
Implementation: cepgen::strfun::Shamov
This model is designed for soft, low-mode parameter:
SuriYennie, the standard, Suri and Yennie continuum (see below) ;RealRes, using a linear grid interpolation of the real photon cross section forRealResAndNonRes, like the earlier, and using the Suri and Yennie non-resonant contribution ;RealAndSuriYennieNonRes, using the Suri and Yennie non-resonant contribution ;RealAndFitNonRes, like theRealResAndNonRes, but using a fit for the non-resonant contributions.
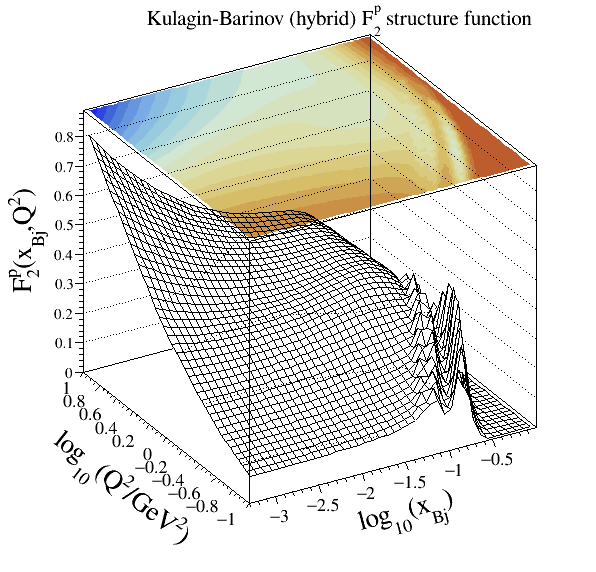
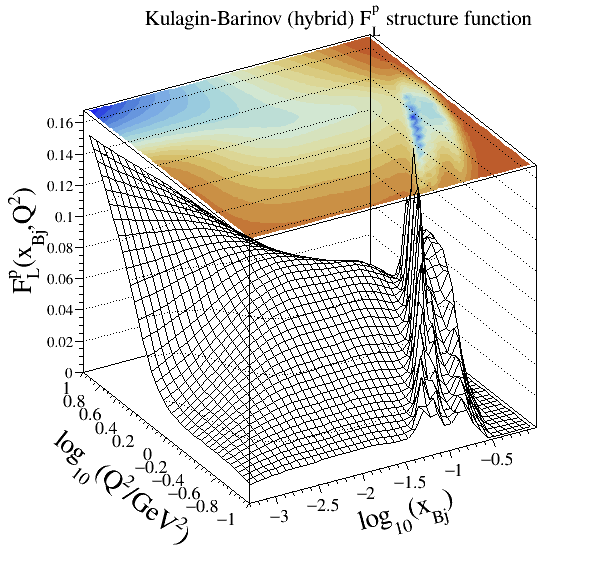
Kulagin-Barinov#
Note
Legacy code:
303Structure functions modelled:
Reference:
Implementation: cepgen::strfun::KulaginBarinov
Resonances are modelled through Breit-Wigner contributions from five states. For the DIS part, a higher twist correction is available from a global QCD fit.
Bodek-Kang-Xu#
Note
Legacy code:
304Structure functions modelled:
Reference:
Implementation: cepgen::strfun::BodekKangXu
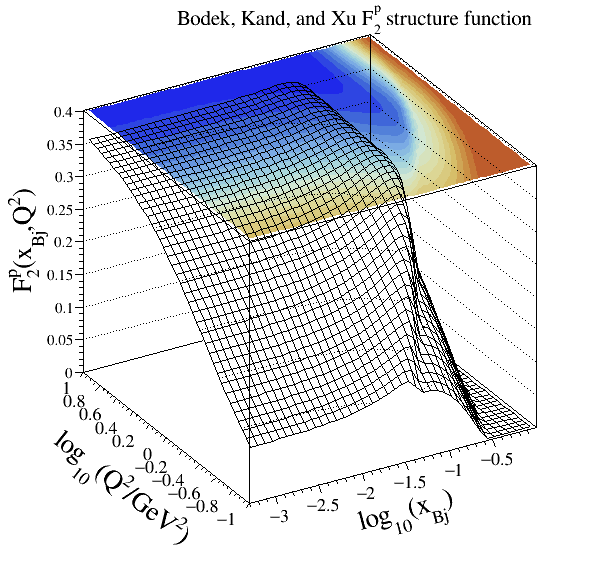
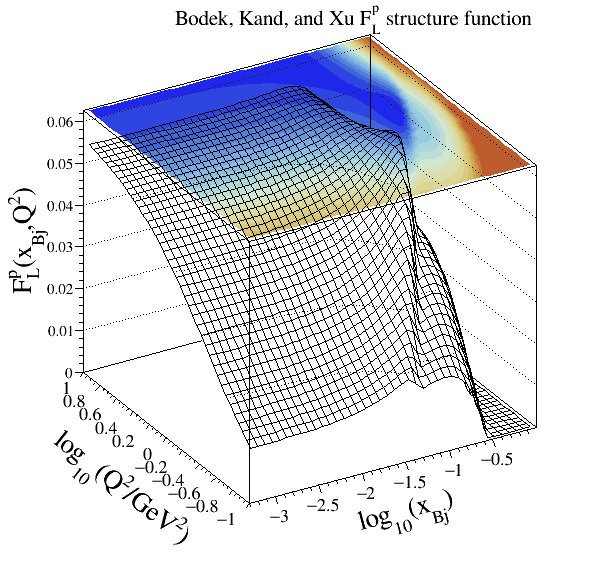
Continuum models#
Suri-Yennie#
Note
Legacy code:
11(and12for the alternative parameterisation)Structure functions modelled:
Reference:
Implementations: cepgen::strfun::SuriYennie and cepgen::strfun::SuriYennieAlt
Module parameters: main and alternative parameterisations
This set was used as a standard option in the LPAIR event generator. It provides a reasonable description of SLAC data in the resonance and continuum regions.
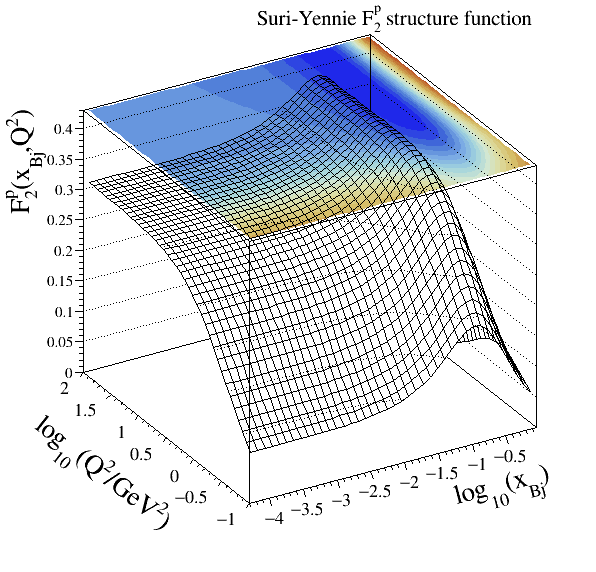
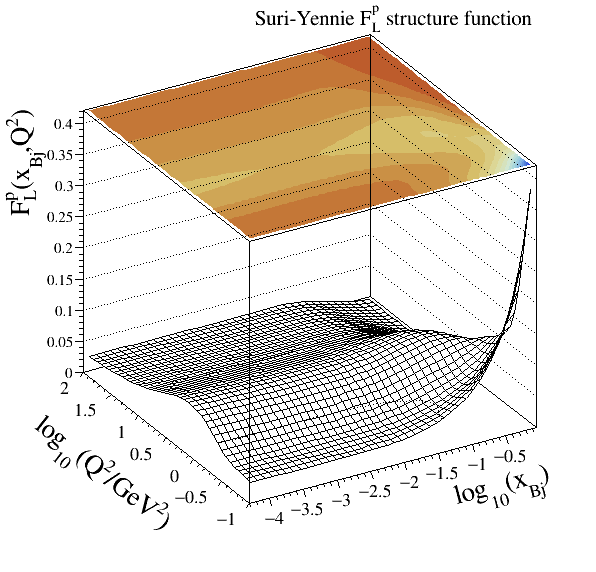
Szczurek-Uleshchenko#
Note
Legacy code:
12Structure function modelled:
Reference:
Implementation: cepgen::strfun::SzczurekUleshchenko, relying on the GRV Fortran interpolation subroutine
This set puts an emphasis on the low-to-intermediate
Block-Durand-Ha#
Note
Legacy code:
13Structure function modelled:
Reference:
Implementation: cepgen::strfun::BlockDurandHa
ALLM parameterisation#
Note
Structure function modelled:
References:
A full reference of this parameterisation by Abramowicz et al. can be found in (
ALLM91) and (ALLM97). The HERMES Collaboration refits of this modelling, labelledGD07pandGD11pmay be found in .Parameterisations:
ALLM91
Legacy code:
201Implementation: cepgen::strfun::ALLM91
ALLM97
Legacy code:
202Implementation: cepgen::strfun::ALLM97
GD07p
Legacy code:
203Implementation: cepgen::strfun::GD07p
GD11p
Legacy code:
204Implementation: cepgen::strfun::GD11p
HHTALLM
Legacy code:
206Implementation: cepgen::strfun::HHTALLM
HHTALLMFT
Legacy code:
207Implementation: cepgen::strfun::HHTALLMFT
In this continuum region modelling the
with
with the slowly-varying function
and the modified Bjorken-
The six functionals
for the pomeron part, and
for the reggeon subset.
Currently, four tunings of the 23 model parameters are embedded within CepGen:
Parameter |
Units |
ALLM91 |
ALLM97 |
GD07p |
GD11p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
GeV |
0.30508 |
0.31985 |
0.454 |
0.5063 |
|
GeV |
10.676 |
49.457 |
30.7 |
34.75 |
|
GeV |
0.20623 |
0.15052 |
0.117 |
0.03190 |
|
GeV |
0.27799 |
0.52544 |
1.15 |
1.374 |
|
GeV |
0.06527 |
0.06527 |
0.06527 |
0.06527 |
|
- |
-0.04503 |
-0.0808 |
-0.105 |
-0.11895 |
|
- |
-0.36407 |
-0.44812 |
-0.495 |
-0.4783 |
|
- |
8.17091 |
1.1709 |
1.29 |
1.353 |
|
- |
0.49222 |
0.36292 |
-1.42 |
1.0833 |
|
- |
0.52116 |
1.8917 |
4.51 |
2.656 |
|
- |
3.5515 |
1.8439 |
0.551 |
1.771 |
|
- |
0.26550 |
0.28067 |
0.339 |
0.3638 |
|
- |
0.04856 |
0.22291 |
0.127 |
0.1211 |
|
- |
1.04682 |
2.1979 |
1.16 |
1.166 |
|
- |
0.60408 |
0.584 |
0.374 |
0.3425 |
|
- |
0.17353 |
0.37888 |
0.998 |
1.0603 |
|
- |
1.61812 |
2.6063 |
0.775 |
0.5164 |
|
- |
1.26066 |
0.01147 |
2.71 |
-10.408 |
|
- |
1.83624 |
3.7582 |
1.83 |
14.857 |
|
- |
0.81141 |
0.49338 |
1.26 |
0.07739 |
|
- |
0.67639 |
0.80107 |
0.838 |
1.3633 |
|
- |
0.49027 |
0.97307 |
2.36 |
2.256 |
|
- |
2.66275 |
3.4942 |
1.77 |
2.209 |
The ALLM91 tuning is fitted from all pre-HERA data points available.
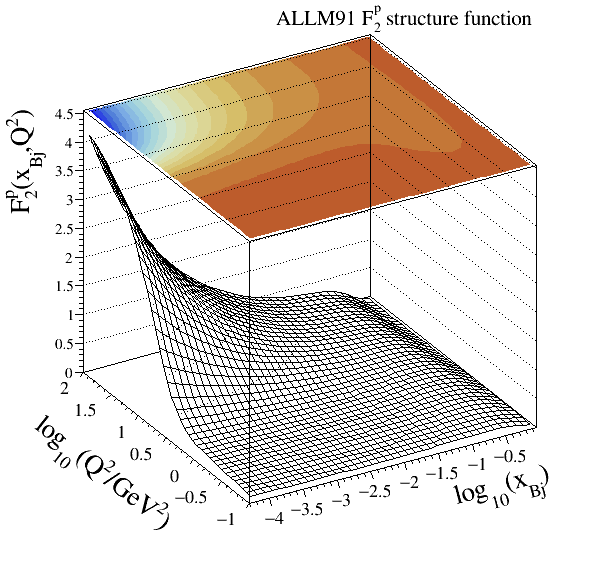

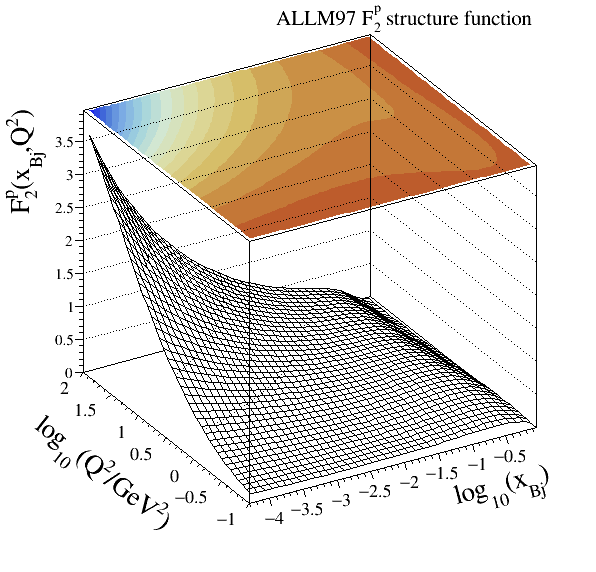
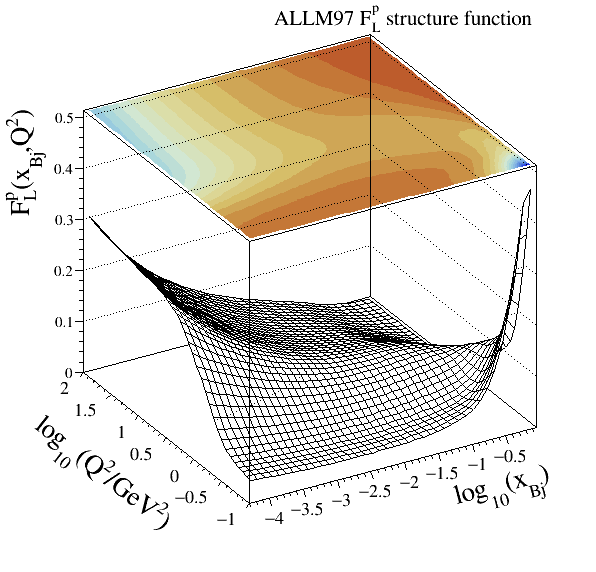
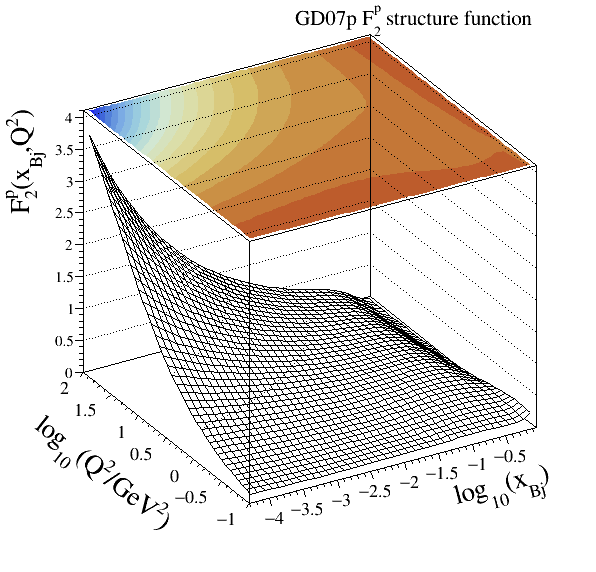
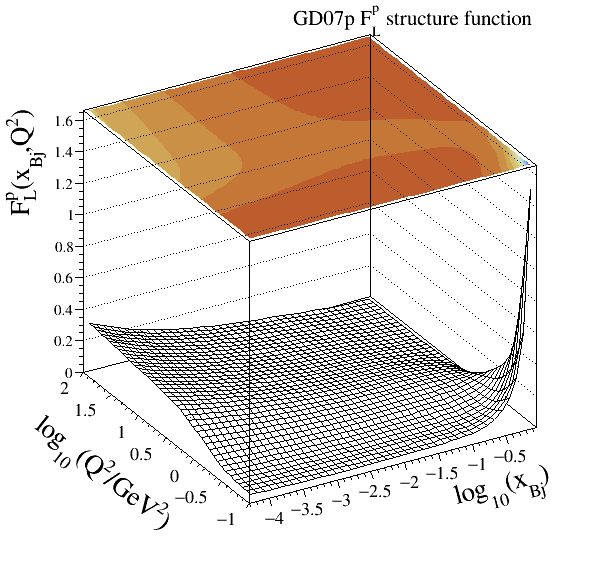
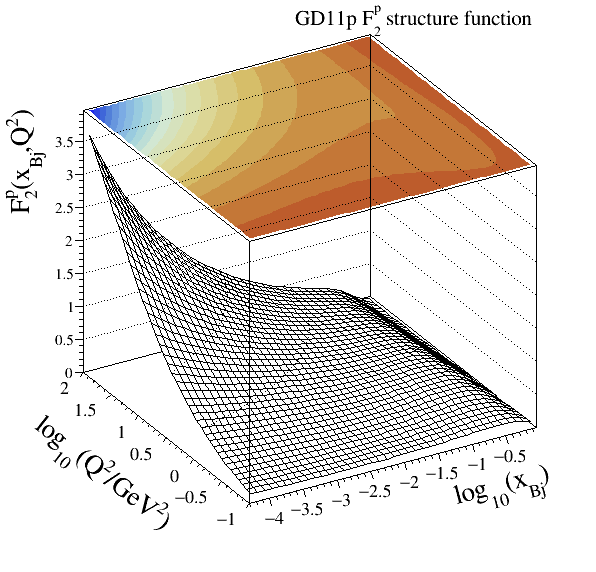
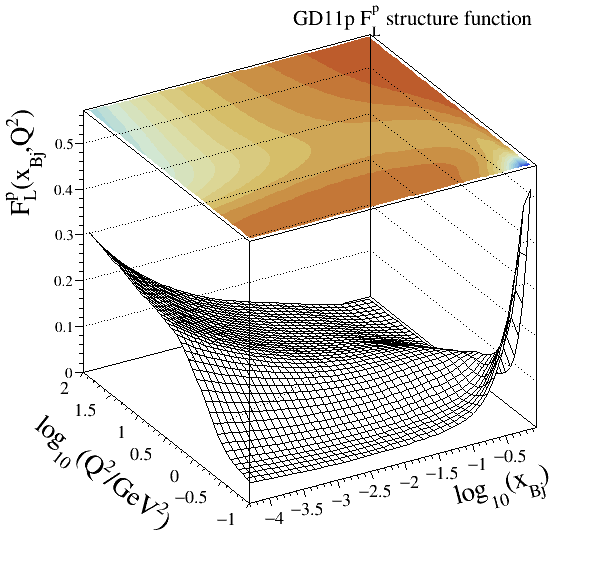
Resonance models#
Fiore-Brasse#
Note
Legacy code:
101(core), and104(alternative)Structure function modelled:
References:
Implementation: cepgen::strfun::FioreBrasse, and cepgen::strfun::FioreBrasseAlt
Modules parameters: core and alternative parameterisations
This parameterisation gives a very good description of photoabsorption in the resonance region from low to large
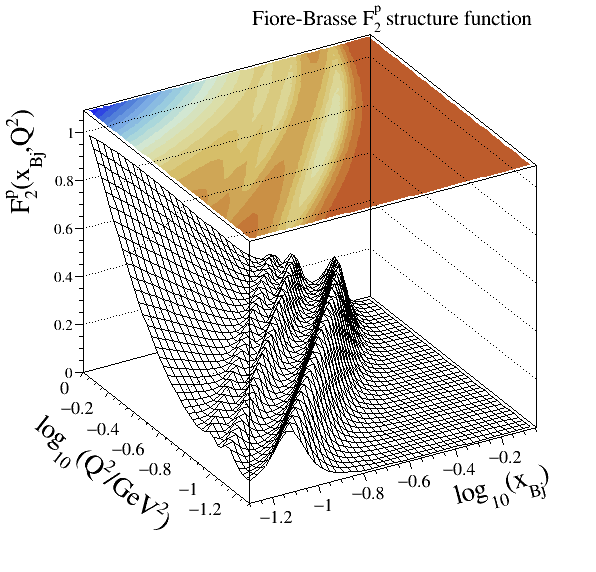
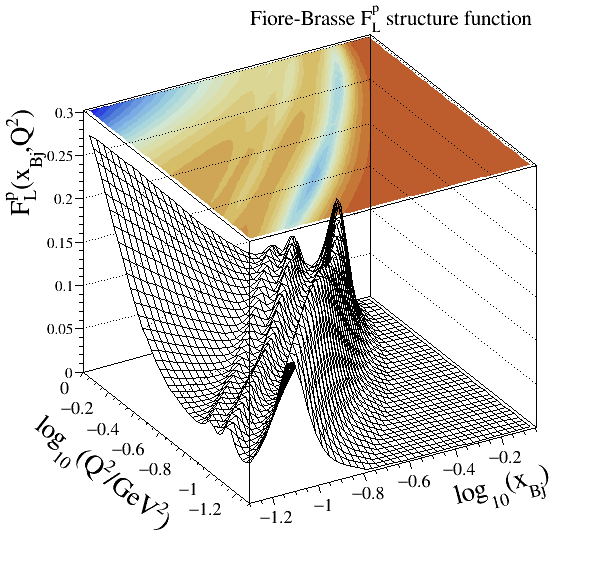
Christy-Bosted#
Note
Legacy code:
102Structure functions modelled:
Reference:
Implementation: cepgen::strfun::ChristyBosted
The set developed by M.E. Christy and P.E. Bosted is emphasised on the very-low
inclusive inelastic (up to
photoproduction at
DIS data at high-
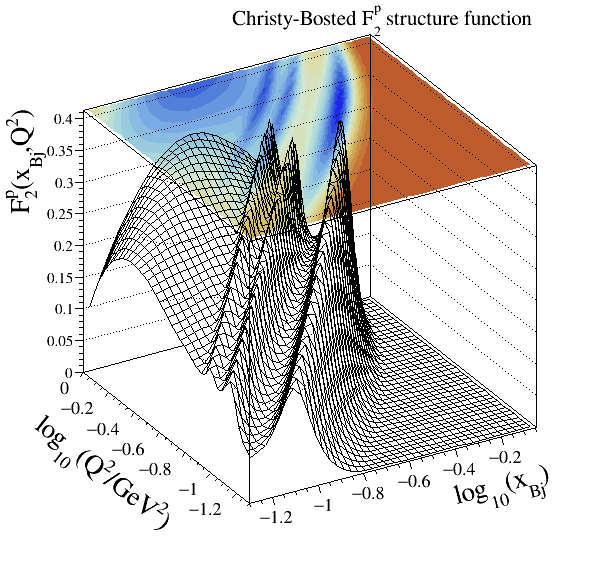
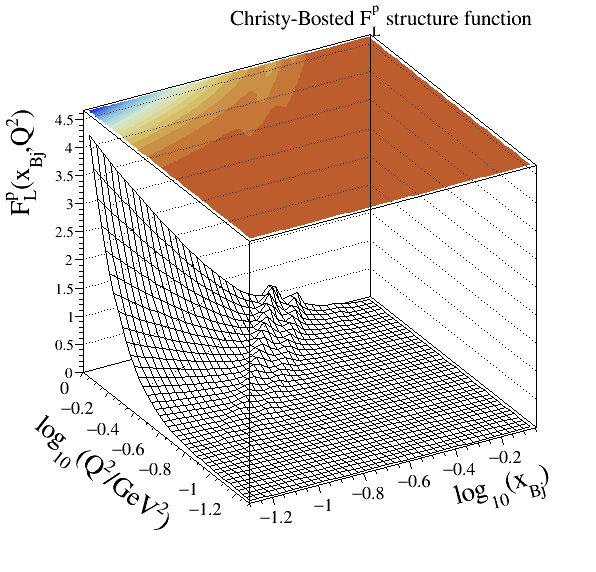
CLAS#
Note
Legacy code:
103Structure functions modelled:
Reference:
Implementation: cepgen::strfun::CLAS
Perturbative models#
MSTW grid#
Warning
doxygenclass: Cannot find class “mstw::Grid” in doxygen xml output for project “CepGen” from directory: /Documentation/build/xml
External interfaces#
Several other models can also be interfaced through a base partonic structure functions interface allowing the conversion of PDFs into
-
class PartonicParameterisation : public Parameterisation#
The conversion of quark/gluon PDF content into
LHAPDF interface#
Note
Legacy code:
401(“standard” parameterisation), or a more complex scheme: : The legacy-equivalent signature follows the convention1MSSSSSS, where:Mspecifies the set of partons included in the sum rule: : -0: all partons,1: valence quarks only, and2: sea quarks only.
SSSSSSis the integer LHAPDF ID code for the selected PDF set.
Structure function modelled:
Reference:
Implementation: cepgen::strfun::LHAPDFPartonic
APFEL++ interface#
Note
Legacy code:
405Structure function modelled:
Reference:
Implementation: cepgen::apfelpp::EvolutionStructureFunctions
This interface to the APFEL++ C++ rewriting of the famous APFEL library covers the computation of order-0/1/2/3 perturbative